Python gRPC Guide
Introduction
gRPC stands for Google Remote Procedure Call.
- gRPC is based on HTTP/2 and Protocol.
- gRPC is well suited for microservices architecture where different services are written in different languages.
- gRPC is language agnostic, meaning it can be used with gRPC supported languages.
- gRPC allows to call methods on a remote server as if it were a local object.
Useful Resources:
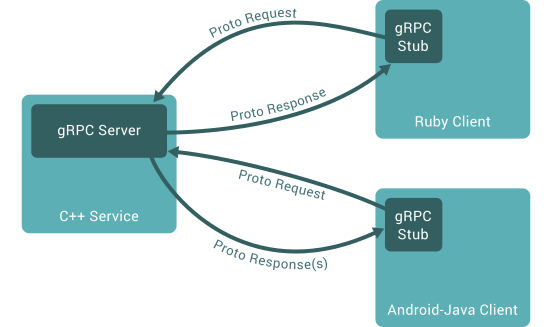
Rough Architecture of gRPC
gRPC Python
Installation
Install the required packages for gRPC Python. grpcio and grpcio-tools are the main packages required for gRPC
Python.
using pip
pip install grpcio grpcio-tools
or using poetry
poetry add grpcio grpcio-tools
Quick Start
-
Create and update a sample proto file
greet.proto.importantRefer
python/src/gRPC/protos/greet.protofrom https://github.com/shangar-t-a/keys-personal-wiki -
Run the following command to generate server and client code from the proto file.
# Template (Not for direct Execution)
python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I <protos_dir> --python_out=<output_dir> --grpc_python_out=<output_dir> <proto_file_dir>using pip
python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I ../protos --python_out=. --grpc_python_out=. ../protos/greet.protoor using poetry
poetry run python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I ../protos --python_out=. --grpc_python_out=. ../protos/greet.proto -
Verify if the command generated the required files
greet_pb2.pyandgreet_pb2_grpc.pyin the output directory. -
Basic server implementation.
importantRefer
python/src/gRPC/greet_server.pyfrom https://github.com/shangar-t-a/keys-personal-wikiPoints to be considered:
- Create a class that inherits from the generated
greet_pb2_grpc.GreeterServicer. Good practice to name it asGreeterServicer(same as the service name in the proto file). - Implement the methods defined in the proto file.
- Define a
servefunction that does the following:- Create a gRPC server.
grpc.server(futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10)). - Add the created servicer to the server.
greet_pb2_grpc.add_GreeterServicer_to_server(GreeterServicer(), server). - Add insecure port to the server.
server.add_insecure_port("localhost:50051"). - Start the server.
server.start(). - Wait for termination.
server.wait_for_termination().
- Create a gRPC server.
- Create a class that inherits from the generated
-
Basic client implementation.
importantRefer
python/src/gRPC/greet_client.pyfrom https://github.com/shangar-t-a/keys-personal-wikiPoints to be considered:
- Create a
runfunction that does the following:- Create a channel with port from the server.
grpc.insecure_channel("localhost:50051"). Best practice to usewithstatement for the channel. - Create a stub.
stub = greet_pb2_grpc.GreeterStub(channel).
- Create a channel with port from the server.
- Create a
-
Client Implementation.
importantRefer
python/src/gRPC/greet_client.pyfrom https://github.com/shangar-t-a/keys-personal-wikiPoints to be considered:
- Client will create a request object defined in the proto file.
- Call the required server method on the stub with the request object and get the response.
-
Server Implementation.
importantRefer
python/src/gRPC/greet_server.pyfrom https://github.com/shangar-t-a/keys-personal-wikiPoints to be considered:
- Server will implement the methods defined in the proto file.
- Create a response object defined in the proto file.
- Return the response object.
-
High level overview of different types of RPCs:
- Unary RPC:
- Client: Create request -> Call server method -> Get response.
- Server: Implement server method -> Create response -> Return response.
- Server Side Streaming RPC:
- Client: Create request -> Call server method -> Get multiple responses.
- Server: Implement server method -> Create and Yield multiple responses.
- Client Side Streaming RPC:
- Client: Create multiple requests (Iterator) -> Call server method -> Get response.
- Server: Implement server method -> Process multiple requests (Iterator) -> Create response -> Return response.
- Bidirectional Streaming RPC:
- Client: Create multiple requests (Iterator) -> Call server method -> Get multiple responses.
- Server: Implement server method -> Process multiple requests (Iterator) -> Create and Yield multiple responses.
- Unary RPC: